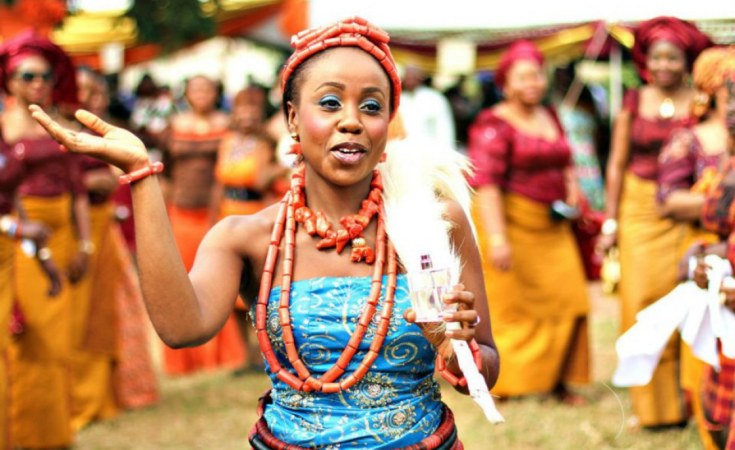
Over 250 ethnic groups thrive within Nigeria, making it one of Africa’s most ethnically diverse countries. Among these ethnic groups, some of the oldest tribes in Nigeria have survived for centuries, passing down their rich heritage despite the pressures of modernization.
Furthermore, these tribes have protected their traditions and maintained their ways of life, reflecting their resilience.
In this article, we dive into the histories of the five oldest tribes in Nigeria, exploring how they have upheld their cultural legacies.
1. The Nok Tribe
The Nok people are widely recognized as one of the oldest tribes in Nigeria. They lived around the area now known as Northern Nigeria. The Nok civilization dates back to around 1000 BC, making it one of the earliest known cultures in West Africa.
The Nok people are famous for their advanced artistry, particularly their terracotta sculptures. These sculptures, often depicting human figures, animals, and mythical creatures, are intricate and detailed.
Archaeologists have found these artifacts in present-day Kaduna, Jos, and parts of Kwara State.
Historical Contributions:
- The Nok tribe is credited with pioneering iron smelting in West Africa.
- They were skilled in making tools, weapons, and ornaments using iron.
- Their artistic influence can still be seen in the craftsmanship of modern Nigerian tribes.
Though the Nok civilization eventually faded, its influence remains significant. The tribe’s artistic legacy provides insight into the early development of societies in Nigeria.
2. The Yoruba Tribe
The Yoruba tribe is one of the largest and most influential ethnic groups in Nigeria. Their history dates back over a thousand years, with roots tracing to the ancient city of Ile-Ife. According to Yoruba mythology, Ile-Ife is the birthplace of humanity, where the world began.
The Yorubas have a well-organized society with a rich cultural heritage. They are known for their elaborate festivals, colorful attire, and intricate beadwork. The Yoruba people are also renowned for their contributions to art, music, and religion.
Cultural Significance:
The Yoruba are famous for their traditional religion, which has influenced spiritual practices across the world, especially in the Americas.
- They have a rich pantheon of gods known as “Orishas,” who govern different aspects of life.
- The Yoruba language and culture have spread beyond Nigeria to countries like Brazil, Cuba, and the United States due to the transatlantic slave trade.
The Yorubas have maintained a strong cultural identity, preserving their language, customs, and traditions over the centuries.
3. The Igbo Tribe
The Igbo people are another ancient and significant ethnic group in Nigeria. The Igbos primarily inhabit the southeastern region of Nigeria.
Historians believe that the Igbo civilization dates back to 9th century AD, but their roots may stretch much further into antiquity.
The Igbos are known for their entrepreneurial spirit, love for education, and democratic systems of governance.
Historically, they practiced a decentralized system of government where communities were ruled by elders and title holders. This system, known as “Igbo-Ukwu,” is one of the oldest forms of democracy in Africa.
Notable Achievements:
- The Igbo are skilled in arts and crafts, particularly in pottery, weaving, and wood carving.
- They are famous for their mask festivals, colorful dances, and masquerade performances.
- The Igbo language, customs, and traditions have been preserved despite colonization and the Nigerian Civil War.
The Igbos have a rich cultural heritage that continues to influence Nigerian culture and beyond.
4. The Kanuri Tribe
The Kanuri people are predominantly found in northeastern Nigeria, particularly in Borno State. They are one of the oldest tribes in Nigeria, with their roots tracing back to the Kanem-Bornu Empire, which existed as early as the 9th century AD.
This empire was a powerful Islamic state that played a significant role in West African trade, politics, and religion.
The Kanuri were instrumental in spreading Islam in Nigeria, and today, most of them practice the Islamic faith. They are known for their elaborate traditional ceremonies, especially during Islamic festivals.
Historical Contributions:
- The Kanuri people contributed to the development of education and trade in the region, establishing schools and learning centers.
- They were skilled horsemen and warriors, which helped them defend their empire against invasions.
- The Kanuri language remains widely spoken in Borno and parts of neighboring countries like Niger and Chad.
Despite the challenges of modern times, including the impact of insurgencies in the northeast, the Kanuri people continue to uphold their traditions.
5. The Fulani Tribe
The Fulani, also known as the Fula or Fulbe, are among the oldest and most widely spread ethnic groups in West Africa. Fulani people are traditionally nomadic herders, traders, and warriors.
Their presence in Nigeria dates back to the 11th century when they began migrating from the Senegambia region.
The Fulani are known for their distinctive cultural practices, including their elegant clothing, rich music, and intricate hairstyles.
They played a major role in the spread of Islam in Nigeria, especially through the Fulani Jihad led by Usman dan Fodio in the early 19th century.
Cultural Highlights:
- The Fulani are famous for their “Wuro,” traditional settlements where they practice a nomadic lifestyle.
- They have a unique cultural festival known as “Sharo,” where young men undergo a public flogging ceremony to prove their manhood.
- The Fulani language, known as Fulfude, is spoken across many West African countries.
Today, while many Fulani have settled in towns and cities, a significant number still maintain their pastoral lifestyle.
Nigeria’s oldest tribes have significantly shaped the country’s cultural, social, and historical landscape. Each tribe has preserved its unique identity, contributing to the rich tapestry of Nigerian culture.
Nonetheless, from the Nok people’s ancient artistry to the Fulani’s enduring nomadic traditions, these tribes continue to inspire pride and unity among Nigerians.
Understanding the history and contributions of these tribes helps to appreciate Nigeria’s diverse heritage. These tribes have not only survived the test of time but have also influenced many aspects of Nigerian life, from language to religion and art.
Read more articles on culture here.


 DRINKS7 days ago
DRINKS7 days ago
 BUSINESS5 days ago
BUSINESS5 days ago
 TRAVEL6 days ago
TRAVEL6 days ago
 FOOD6 days ago
FOOD6 days ago
 MOVIES4 days ago
MOVIES4 days ago
 INTERNATIONAL2 days ago
INTERNATIONAL2 days ago
 SEX6 days ago
SEX6 days ago
 MOVIES5 days ago
MOVIES5 days ago