LIFESTYLE
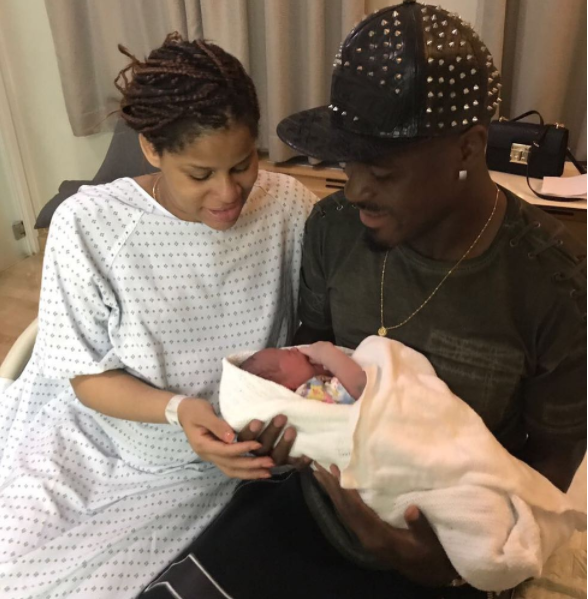
Footballer Emmanuel Emenike’s Wife Iheoma Nnadi Reveals Why She Won’t Show Their Daughter’s Face On The Internet
Published
6 years agoon
By
FAB

Super Eagles player, Emmanuel Emenike and his wife Iheoma Nnadi have posted photos of their daughter on Instagram story but never shown her face because “the internet is a very scary place”
In a question and answer session with her fans and followers, the former beauty queen said that they are not ready as the internet is a very scary place to be putting their daughter’s face.
“I am very protective of my baby” she added.


TRAVEL
Here Are The 7 Most Ancient Countries On Earth
Published
3 months agoon
January 12, 2025By
wpadminee
The oldest countries in the world stand as remarkable testaments to human civilisation, each containing landscapes and monuments that narrate stories spanning thousands of years.
These ancient territories, recognised today as some of the oldest countries in the world, preserve the foundations of early human settlements, technological innovations, and the emergence of complex social structures.
When we examine these ancient lands, we discover intricate tapestries of human achievement, where early societies developed sophisticated systems of writing, architecture, and governance.
Archaeological evidence reveals how these civilisations mastered agriculture, created magnificent works of art, and established trading networks that would influence cultures across continents.
The legacy of these oldest countries in the world continues to influence modern society through their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, philosophy, and religious thought.
Each archaeological discovery within their borders provides new insights into how our ancestors lived, worshipped, and built communities that would evolve into the nations we know today.
These enduring civilisations, which have maintained cultural continuity through millennia, demonstrate humanity’s remarkable capacity for resilience and adaptation.
Their ancient monuments, texts, and artefacts serve as windows into the past, helping us understand how early societies overcame challenges and developed innovations that would shape human history.
As we prepare to explore seven of these remarkable nations, we witness how their ancient heritage continues to influence contemporary global culture.
1. Egypt

Egypt stands proudly as one of the oldest countries in the world, with a remarkable history spanning over 5,000 years.
Renowned as the land of the pharaohs, it introduced iconic marvels such as the Pyramids of Giza, the enigmatic Sphinx, and the intricate system of hieroglyphic writing.
The ancient Egyptians were trailblazers in architecture, mathematics, and medicine, leaving a legacy that continues to influence modern society.
Their awe-inspiring temples and tombs, alongside their contributions to early science and governance, highlight Egypt’s enduring significance as a cradle of civilisation.
2. China

China, another of the oldest countries in the world, boasts a history stretching back more than 4,000 years.
Its ancient dynasties laid the foundation for many groundbreaking inventions. This includes paper, gunpowder, and the compass—tools that transformed human progress.
The Great Wall of China, a colossal feat of engineering, is a powerful symbol of its resilience and grandeur.
Even in the modern era, China remains deeply connected to its rich traditions. From calligraphy to Confucian philosophy, showcasing its enduring cultural and historical importance.
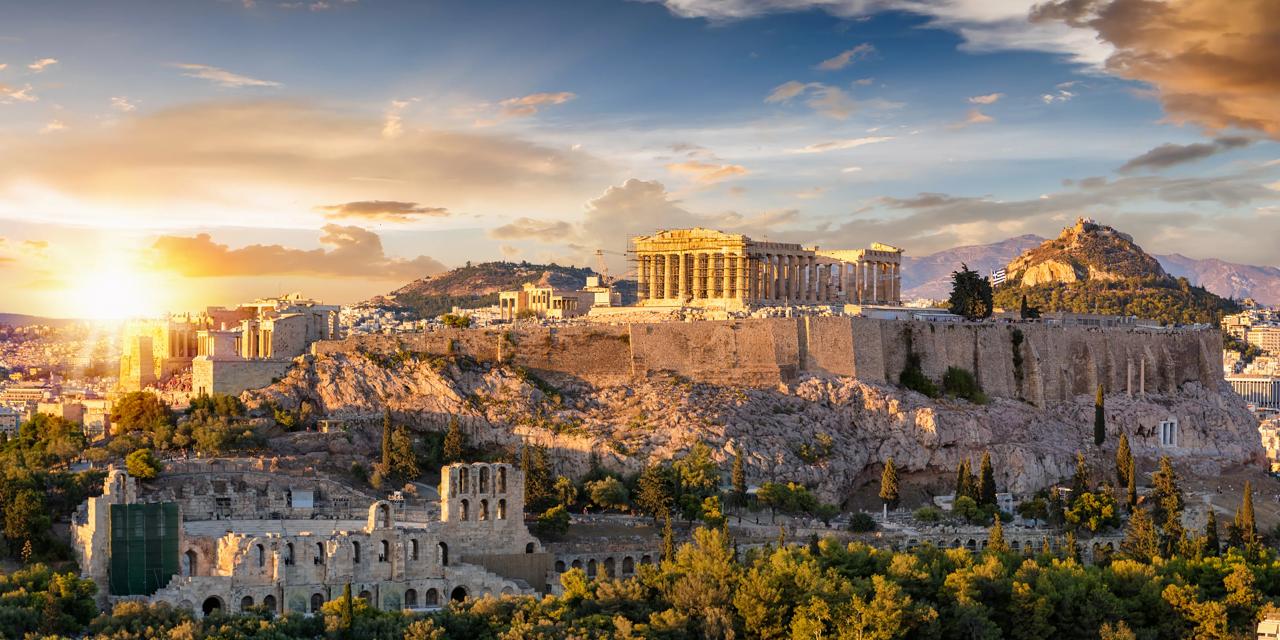
3. Greece
Greece has a history exceeding 3,000 years. She played a pivotal role in shaping the intellectual and cultural framework of the modern world.
Ancient Greece introduced revolutionary ideas that still resonate today. They are often celebrated as the birthplace of democracy, philosophy, and the Olympic Games.
Thinkers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle laid the groundwork for disciplines such as science, politics, and art.
Greece’s iconic ruins, including the Parthenon, are timeless reminders of its innovative spirit and its position among the oldest countries in the world.
4. India

India, home to one of the earliest known civilisations—the Indus Valley Civilisation—holds its place as one of the oldest countries in the world. They have a history spanning over 4,500 years.
This land gave birth to major religions like Hinduism and Buddhism, which have shaped spiritual practices across the globe. Ancient Indian scholars achieved remarkable advancements in literature, mathematics (including the concept of zero), and astronomy.
India’s rich tapestry of history is reflected in its enduring cultural festivals, architectural wonders like the Taj Mahal, and centuries-old traditions.
5. Iran

Iran, historically known as Persia, carries a legacy that stretches back more than 4,000 years. The Persian Empire was once one of the largest and most sophisticated empires in the world. The country introduced significant advancements in governance, art, and architecture.
Persian poetry, from luminaries like Rumi and Hafez, continues to inspire readers worldwide. The intricate designs of Persian carpets and the grandiose palaces of ancient Persia are enduring testaments to the country’s rich cultural heritage.
6. Ethiopia

Ethiopia, often called the cradle of humanity, holds a unique place in world history. Fossil discoveries, such as the famous “Lucy,” suggest that some of the earliest humans originated here.
With over 2,000 years of documented history, Ethiopia is also one of the oldest countries in the world. Remarkably, it is one of the few African nations never colonised, preserving its independence and rich traditions.
Ethiopia’s ancient rock-hewn churches, such as those in Lalibela, and its storied heritage of kingdoms and empires highlight its importance in the annals of human history.
7. Japan
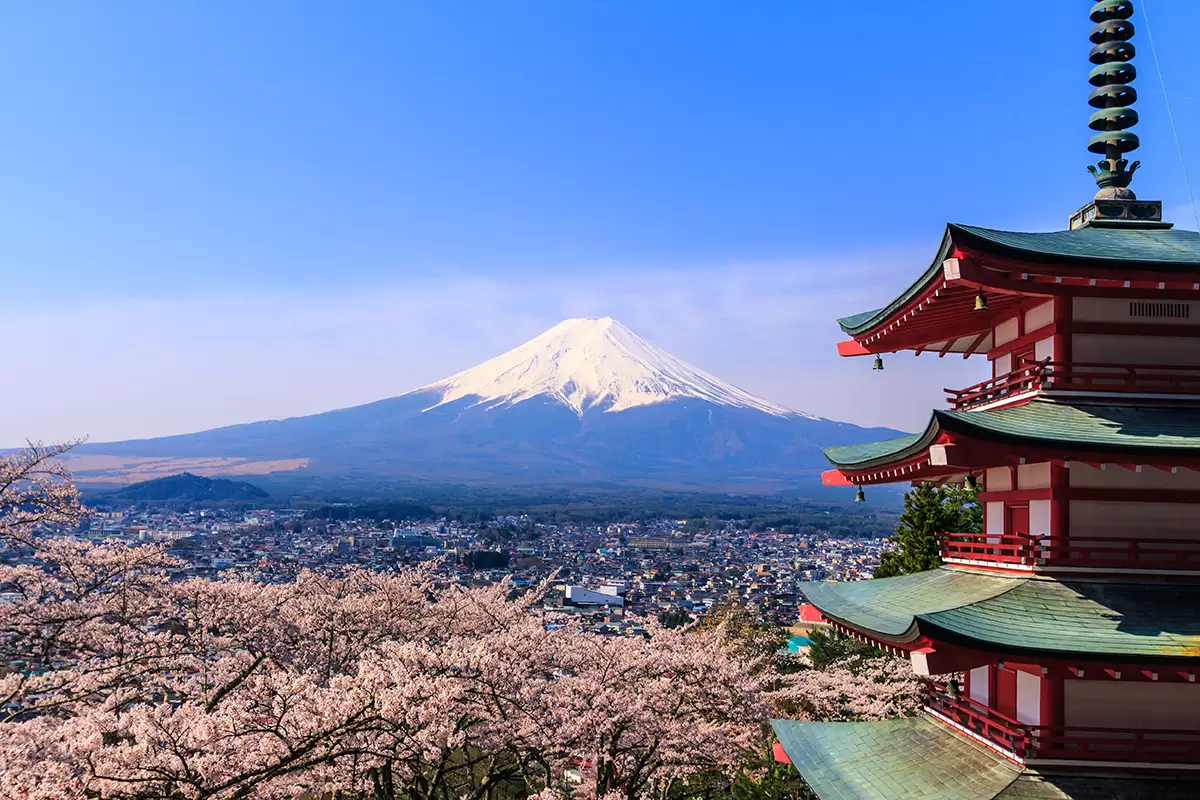

Japan, with a history spanning over 2,000 years, blends ancient customs with cutting-edge innovation. Known as one of the oldest countries in the world, it boasts the world’s longest continuous imperial lineage.
Samurai culture, traditional tea ceremonies, and intricate woodblock art illustrate Japan’s dedication to preserving its historical identity. Simultaneously, the nation has embraced modernity, becoming a global leader in technology and design.
The harmonious balance between its storied past and dynamic present makes Japan a cultural treasure on the global stage.
For similar articles, visit here.
LIFESTYLE
Why Self-Reflection Is More Important Than Resolutions
Published
3 months agoon
January 11, 2025By
wpadminee
Millions of people embark on a yearly ritual: they sit down with a notebook and pen, eager to craft a list of perfect resolutions and forget to do a proper self-reflection.
“This year, I’ll shed those extra pounds,” they declare. “I’ll diligently save more money.” “I’ll finally master the French language.” These aspirations often sound incredibly promising.
However, let’s be realistic – how frequently do we actually achieve these goals? Statistics reveal a sobering truth: most individuals abandon their resolutions by February.
Why does this pattern persist? The answer lies in the resolutions themselves. They typically focus solely on the desired outcome – what we aim to change – without delving into the underlying reasons for this change or identifying the obstacles hindering our progress.
This is where the power of self-reflection comes into play. Instead of hastily making grand promises to ourselves, self-reflection encourages us to pause, introspect, and gain a deeper understanding of our true motivations, ingrained habits, and the challenges that may impede our journey.
Therefore, if you’re weary of repeating the same cycle of annual promises and feeling perpetually stuck, it’s time to consider a different approach.
Self-reflection holds greater significance than resolutions in fostering meaningful personal growth.
1. Self-reflection goes deeper into your motivations.
While resolutions often remain superficial, such as the common goal of “losing weight,” self-reflection compels you to explore the underlying reasons for this desire.
Are you driven by genuine health concerns and a desire to boost your confidence, or are you succumbing to societal pressures to conform to a particular body image?
By probing deeper, self-reflection encourages you to ask critical, albeit uncomfortable, questions. It challenges you to examine the obstacles hindering your progress and determine whether you are genuinely pursuing your own aspirations or merely emulating the resolutions of others.
This introspection fosters a deeper understanding of your “why,” transforming your actions from reactive impulses into intentional, purposeful pursuits.
2. Self-reflection facilitates learning from past experiences.
We often repeat the same mistakes without ever taking the time to analyse what went wrong. Self-reflection provides an invaluable opportunity to review past events without judgment.
For instance, if you failed to save money last year, self-reflection might reveal a lack of spending tracking as the root cause. Alternatively, an unused gym membership could indicate the setting of unrealistic fitness goals.
Instead of hastily embarking on new resolutions, self-reflection encourages you to learn from these patterns, establishing a more solid foundation for future change.
3. It promotes realistic and personalised growth.
Resolutions frequently focus on grand, ambitious outcomes. However, true growth is often subtle and deeply personal. Self-reflection enables you to identify small, meaningful steps that can lead to lasting transformation.
For example, instead of setting the broad goal of “becoming more productive,” self-reflection might reveal that poor time management is your primary obstacle.
Implementing a simple, actionable strategy, such as creating a daily schedule, can significantly impact your productivity.
4. Alleviates pressure and reduces guilt.
Resolutions often come with an inherent sense of urgency and a looming deadline. By March, the pressure to succeed can mount, leading to feelings of guilt and self-doubt as we inevitably fall short of our lofty goals.
In contrast, self-reflection is an ongoing, iterative process. It encourages you to acknowledge and celebrate small victories while extending compassion to yourself during setbacks. Growth is rarely linear, and self-reflection acknowledges this reality.
5. Strengthens self-awareness.
At its core, self-reflection is about gaining a deeper understanding of oneself. By exploring your strengths, weaknesses, and the triggers that influence your behaviour, you become better equipped to navigate challenges and make choices that align with your authentic self.
Therefore, instead of rushing to compile a lengthy list of resolutions for the year, take a moment to turn your attention inward. You may be surprised to discover that the answers you seek reside within you all along.
If you found this article helpful, visit here for more.
ENTERTAINMENT
Tems, Ayo Edebiri, Wizkid & More Nominated For The 56th NAACP Image Awards
Published
3 months agoon
January 8, 2025By
Reporter
The 56th NAACP Image Awards have unveiled their nominations. It highlights various exceptional talents. These talents include Nigerian stars Tems, Ayo Edebiri, Burna Boy, and Wizkid, alongside British Nigerian actress Cynthia Erivo.
The awards ceremony, set to take place on February 22nd, will be broadcast live on BET and CBS from the Pasadena Civic Center. It will celebrate “Our Stories, Our Culture, Our Excellence.”
Usher and Burna Boy received a nomination for “Outstanding Duo, Group or Collaboration (Contemporary)”. It was for their captivating song “Coming Home.”
Meanwhile, Wizkid earned a nod in the “Outstanding International Song” category for his soulful track “Piece of My Heart.” The track features the talented Brent Faiyaz. Joining Wizkid in this category is Tems, recognized for her mesmerizing song “Love Me JeJe.”
Rising star Tyla received a well-deserved nomination for “Outstanding New Artist.” Also, Ayo Edebiri led the pack with an impressive five nominations.
Her nominations include “Outstanding Actress in a Comedy Series,” showcasing her comedic prowess. Edebiri also garnered recognition for her exceptional voiceover work.
In the animated category, Disney+’s captivating series “Iwájú” received a nomination for “Outstanding Animated Series.” Further, this solidified the series in the realm of animated excellence.
See the full list of nominations for the 56th NAACP Image Awards below.
Entertainer of the Year Nominees
- Cynthia Erivo
- Keke Palmer
- Kendrick Lamar
- Kevin Hart
- Shannon Sharpe
Outstanding Social Media Personality of the Year Nominees
- Kai Cenat
- Keith Lee
- RaeShanda Lias
- Shirley Raines
- Tony Baker
Motion Pictures Categories
Outstanding Motion Picture
- “Bad Boys: Ride or Die” (Sony Pictures)
- “Bob Marley: One Love” (Paramount Pictures)
- “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- “The Six Triple Eight” (Netflix)
- “Wicked” (Universal Pictures)
Outstanding Actor in a Motion Picture
- André Holland — “Exhibiting Forgiveness” (Roadside Attractions)
- Colman Domingo — “Sing Sing” (A24)
- John David Washington — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- Kingsley Ben-Adir — “Bob Marley: One Love” (Paramount Pictures)
- Martin Lawrence — “Bad Boys: Ride or Die” (Sony Pictures)
Outstanding Actress in a Motion Picture
- Cynthia Erivo — “Wicked” (Universal Pictures)
- Kerry Washington — “The Six Triple Eight” (Netflix)
- Lashana Lynch — “Bob Marley: One Love” (Paramount Pictures)
- Lupita Nyong’o — “A Quiet Place: Day One” (Paramount Pictures)
- Regina King — “Shirley” (Netflix)
Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Motion Picture
- Brian Tyree Henry — “The Fire Inside” (Amazon MGM Studios)
- Corey Hawkins — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- David Alan Grier — “The American Society of Magical Negroes” (Focus Features)
- Denzel Washington — “Gladiator II” (Paramount Pictures)
- Samuel L. Jackson — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Motion Picture
- Aunjanue Ellis-Taylor — “Exhibiting Forgiveness” (Roadside Attractions)
- Aunjanue Ellis-Taylor — “Nickel Boys” (Orion Pictures/Amazon MGM Studios)
- Danielle Deadwyler — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- Ebony Obsidian — “The Six Triple Eight” (Netflix)
- Lynn Whitfield — “Albany Road” (Faith Filmworks)
Outstanding Independent Motion Picture
- “Albany Road” (Faith Filmworks)
- “Exhibiting Forgiveness” (Roadside Attractions)
- “Rob Peace” (Republic Pictures)
- “Sing Sing” (A24)
- “We Grown Now” (Sony Pictures Classics)
Outstanding International Motion Picture
- “El lugar de la otra” (Netflix)
- “Emilia Pérez” (Netflix)
- “Memoir of a Snail” (IFC Films)
- “The Seed of the Sacred Fig” (NEON)
- “The Wall Street Boy, Kipkemboi” (ArtMattan Films)
Outstanding Breakthrough Performance in a Motion Picture
- Brandon Wilson — “Nickel Boys” (Orion Pictures/Amazon MGM Studios)
- Clarence Maclin — “Sing Sing” (A24)
- Danielle Deadwyler — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- Ebony Obsidian — “The Six Triple Eight” (Netflix)
- Ryan Destiny — “The Fire Inside” (Amazon MGM Studios)
Outstanding Ensemble Cast in a Motion Picture
- “Bob Marley: One Love” (Paramount Pictures)
- “The Book of Clarence” (Sony Pictures)
- “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- “The Six Triple Eight” (Netflix)
- “Wicked” (Universal Pictures)
Outstanding Animated Motion Picture
- “Inside Out 2” (Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures)
- “Kung Fu Panda 4” (DreamWorks Animation)
- “Moana 2” (Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures)
- “Piece by Piece” (Focus Features)
- “The Wild Robot” (DreamWorks Animation)
Outstanding Character Voiceover Performance – Motion Picture
- Aaron Pierre — “Mufasa: The Lion King” (Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures)
- Anika Noni Rose — “Mufasa: The Lion King” (Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures)
- Ayo Edebiri — “Inside Out 2” (Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures)
- Blue Ivy Carter — “Mufasa: The Lion King” (Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures)
- Lupita Nyong’o — “The Wild Robot” (DreamWorks Animation)
Outstanding Short Form (Live Action)
- “Chocolate with Sprinkles” (AFI)
- “Definitely Not a Monster”
- “If They Took Us Back”
- “My Brother & Me” (MeowBark Films)
- “Superman Doesn’t Steal”
Outstanding Short Form (Animated)
- “if(fy)” (OTB/The Hidden Hand Studios)
- “Nate & John” (Unity Animation Project, LLC)
- “Peanut Headz: Black History Toonz ‘Jackie Robinson’” (Exhibit Treal Studios)
- “Self” (Pixar Animation Studios)
- “Walk in the Light” (419 Studios)
Outstanding Breakthrough Creative (Motion Picture)
- David Fortune — “Color Book” (Tribeca Studios)
- Malcolm Washington — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- RaMell Ross — “Nickel Boys” (Orion Pictures/Amazon MGM Studios)
- Titus Kaphar — “Exhibiting Forgiveness” (Roadside Attractions)
- Zoë Kravitz — “Blink Twice” (Amazon MGM Studios)
Outstanding Youth Performance in a Motion Picture
- Anthony B. Jenkins — “The Deliverance” (Netflix)
- Blake Cameron James — “We Grown Now” (Sony Pictures Classics)
- Jeremiah Daniels — “Color Book” (Tribeca Studios)
- Percy Daggs IV — “Never Let Go” (Lionsgate)
- Skylar Aleece Smith — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
Outstanding Cinematography in a Motion Picture
- Andrés Arochi — “Longlegs” (NEON)
- Jomo Fray — “Nickel Boys” (Orion Pictures/Amazon MGM Studios)
- Justin Derry — “She Taught Love” (Andscape)
- Lachlan Milne — “Exhibiting Forgiveness” (Roadside Attractions)
- Rob Hardy — “The Book of Clarence” (Sony Pictures)
Television and Streaming Categories
Outstanding Comedy Series
- “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- “How to Die Alone” (Hulu)
- “Poppa’s House” (CBS)
- “The Neighborhood” (CBS)
- “The Upshaws” (Netflix)
Outstanding Actor in a Comedy Series
- Cedric The Entertainer — “The Neighborhood” (CBS)
- Damon Wayans — “Poppa’s House” (CBS)
- David Alan Grier — “St. Denis Medical” (NBC)
- Delroy Lindo — “UnPrisoned” (Hulu)
- Mike Epps — “The Upshaws” (Netflix)
Outstanding Actress in a Comedy Series
- Ayo Edebiri — “The Bear” (FX/Hulu)
- Kerry Washington — “UnPrisoned” (Hulu)
- Natasha Rothwell — “How to Die Alone” (Hulu)
- Quinta Brunson — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- Tichina Arnold — “The Neighborhood” (CBS)
Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Comedy Series
- Damon Wayans Jr. — “Poppa’s House” (CBS)
- Giancarlo Esposito — “The Gentlemen” (Netflix)
- Kenan Thompson — “Saturday Night Live” (NBC)
- Tyler James Williams — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- William Stanford Davis — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Comedy Series
- Danielle Pinnock — “Ghosts” (CBS)
- Ego Nwodim — “Saturday Night Live” (NBC)
- Janelle James — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- Sheryl Lee Ralph — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- Wanda Sykes — “The Upshaws” (Netflix)
Outstanding Drama Series
- “9-1-1” (ABC)
- “Bel-Air” (Peacock)
- “Cross” (Amazon Prime Video)
- “Found” (NBC)
- “Reasonable Doubt” (Hulu)
Outstanding Actor in a Drama Series
- Aldis Hodge — “Cross” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Donald Glover — “Mr. & Mrs. Smith” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Harold Perrineau — “From” (MGM+)
- Jabari Banks — “Bel-Air” (Peacock)
- Michael Rainey Jr. — “Power Book II: Ghost” (Starz)
Outstanding Actress in a Drama Series
- Angela Bassett — “9-1-1” (ABC)
- Emayatzy Corinealdi — “Reasonable Doubt” (Hulu)
- Queen Latifah — “The Equalizer” (CBS)
- Shanola Hampton — “Found” (NBC)
- Zoe Saldaña — “Lioness” (Paramount+)
Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Drama Series
- Adrian Holmes — “Bel-Air” (Netflix)
- Cliff “Method Man” Smith — “Power Book II: Ghost” (Starz)
- Isaiah Mustafa — “Cross” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Jacob Latimore — “The Chi” (Paramount+)
- Morris Chestnut — “Reasonable Doubt” (Hulu)
Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Drama Series
- Adjoa Andoh — “Bridgerton” (Netflix)
- Coco Jones — “Bel-Air” (Peacock)
- Golda Rosheuvel — “Bridgerton” (Netflix)
- Lorraine Toussaint — “The Equalizer” (CBS)
- Lynn Whitfield — “The Chi” (Paramount+)
Outstanding Limited Television (Series, Special or Movie)
- “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- “Genius: MLK/X” (National Geographic)
- “Griselda” (Netflix)
- “Rebel Ridge” (Netflix)
- “The Madness” (Netflix)
Outstanding Actor in a Limited Television (Series, Special or Movie)
- Aaron Pierre — “Rebel Ridge” (Netflix)
- Colman Domingo — “The Madness” (Netflix)
- Kelvin Harrison Jr. — “Genius: MLK/X” (National Geographic)
- Kevin Hart — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- Laurence Fishburne — “Clipped” (FX/Hulu)
Outstanding Actress in a Limited Television (Series, Special or Movie)
- Aunjanue Ellis-Taylor — “The Supremes at Earl’s All-You-Can-Eat” (Hulu/Searchlight Pictures)
- Naturi Naughton — “Abducted at an HBCU: A Black Girl Missing Movie” (Lifetime)
- Sanaa Lathan — “The Supremes at Earl’s All-You-Can-Eat” (Hulu/Searchlight Pictures)
- Sofía Vergara — “Griselda” (Netflix)
- Uzo Aduba — “The Supremes at Earl’s All-You-Can-Eat” (Hulu/Searchlight Pictures)
Outstanding Supporting Actor in a Limited Television (Series, Special or Movie)
- Don Cheadle — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- Luke James — “Them: The Scare” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Ron Cephas Jones — “Genius: MLK/X” (National Geographic)
- Samuel L. Jackson — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- Terrence Howard — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
Outstanding Supporting Actress in a Limited Television (Series, Special or Movie)
- Brandy Norwood — “Descendants: The Rise of Red” (Disney+)
- Jayme Lawson — “Genius: MLK/X” (National Geographic)
- Loretta Devine — “Terry McMillan Presents: Tempted By Love” (Lifetime)
- Sanaa Lathan — “Young. Wild. Free.” (BET+)
- Taraji P. Henson — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
Outstanding News/Information (Series or Special)
- “Black Men’s Summit” (BET Media Group)
- “Finding Your Roots with Henry Louis Gates, Jr.” (PBS)
- “Laura Coates Live” (CNN)
- “NewsNight with Abby Phillip” (CNN)
- “The ReidOut” (MSNBC)
Outstanding Talk Series
- “Hart to Heart” (Peacock)
- “Sherri” (Syndicated)
- “Tamron Hall Show” (Syndicated)
- “The Jennifer Hudson Show” (Syndicated)
- “The Shop” Season 7 (YouTube)
Outstanding Reality Program, Reality Competition or Game Show (Series)
- “Celebrity Family Feud” (ABC)
- “Password” (NBC)
- “Rhythm + Flow” (Netflix)
- “The Real Housewives of Potomac” (Bravo)
- “Tia Mowry: My Next Act” (WeTV)
Outstanding Variety Show (Series or Special)
- “BET Awards 2024” (BET Media Group)
- “Deon Cole: Ok, Mister” (Netflix)
- “Jamie Foxx: What Had Happened Was…” (Netflix)
- “Katt Williams: Woke Foke” (Netflix)
- “Saturday Night Live” (NBC)
Outstanding Children’s Program
- “Craig of the Creek” (Cartoon Network)
- “Descendants: The Rise of Red” (Disney+)
- “Gracie’s Corner” (YouTube TV)
- “Sesame Street” (Max)
- “Snoopy Presents: Welcome Home, Franklin” (Apple TV+)
Outstanding Performance by a Youth (Series, Special, Television Movie or Limited Series)
- Caleb Elijah — “Cross” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Graceyn Hollingsworth — “Gracie’s Corner” (YouTube TV)
- Leah Sava Jeffries — “Percy Jackson and the Olympians” (Disney+)
- Melody Hurd — “Cross” (Amazon Prime Video)
- TJ Mixson — “The Madness” (Netflix)
Outstanding Host in a Talk or News/Information (Series or Special) – Individual or Ensemble
- Abby Phillip — “NewsNight with Abby Phillip” (CNN)
- Henry Louis Gates Jr. — “Finding Your Roots with Henry Louis Gates, Jr.” (PBS)
- Jennifer Hudson — “The Jennifer Hudson” (Syndicated)
- Joy Reid — “The Reidout” (MSNBC)
- Sherri Shepherd — “Sherri” (Syndicated)
Outstanding Host in a Reality/Reality Competition, Game Show or Variety (Series or Special) –
Individual or Ensemble
- Alfonso Ribeiro — “Dancing with the Stars” (ABC)
- Keke Palmer — “Password” (NBC)
- Nick Cannon — “The Masked Singer” (FOX)
- Steve Harvey — “Celebrity Family Feud” (ABC)
- Taraji P. Henson — “BET Awards 2024” (BET Media Group)
Outstanding Guest Performance
- Ayo Edebiri — “Saturday Night Live” (NBC)
- Cree Summer — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- Keegan-Michael Key — “Abbott Elementary” (ABC)
- Marlon Wayans — “Bel-Air” (Peacock)
- Maya Rudolph — “Saturday Night Live” (NBC)
Outstanding Animated Series
- “Disney Jr.’s Ariel” (Disney Jr.)
- “Everybody Still Hates Chris” (Comedy Central)
- “Gracie’s Corner” (YouTube TV)
- “Iwájú” (Disney+)
- “Marvel’s Moon Girl and Devil Dinosaur” (Disney Channel)
Outstanding Character Voiceover Performance (Television)
- Angela Bassett — “Orion and the Dark” (Netflix)
- Cree Summer — “Rugrats” (Nickelodeon)
- Cree Summer — “The Legend of Vox Machina” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Dawnn Lewis — “Star Trek: Lower Decks” (Paramount+)
- Keke Palmer — “The Second Best Hospital in the Galaxy” (Amazon Prime Video)
Outstanding Short Form Series or Special – Reality/Nonfiction/Documentary
- “In the Margins” (PBS)
- NCAA Basketball on CBS Sports (CBS)
- “Roots of Resistance” (PBS)
- “SC Featured” (ESPN)
- “The Prince of Death Row Records “(YouTube TV)
Outstanding Breakthrough Creative (Television)
- Ayo Edebiri — “The Bear” (FX/Hulu)
- Diarra Kilpatrick — “Diarra From Detroit” (BET+)
- Maurice Williams — “The Madness” (Netflix)
- Thembi L. Banks — “Young. Wild. Free.” (BET+)
- Vince Staples — “The Vince Staples Show” (Netflix)
Recording Categories
Outstanding New Artist
- Doechii (Capitol Records/Top Dawg Entertainment)
- Myles Smith (RCA Records/Sony Music Entertainment)
- Samoht (Affective Music)
- Shaboozey (American Dogwood/Empire)
- Tyla (Epic Records)
Outstanding Male Artist
- Chris Brown (RCA Records/Chris Brown Entertainment)
- J. Cole (Dreamville/Interscope Records)
- Kendrick Lamar (pgLang, under exclusive license to Interscope Records)
- October London (Death Row Records/gamma.)
- Usher (mega/gamma.)
Outstanding Female Artist
- Beyoncé (Columbia Records/Parkwood Entertainment LLC)
- Coco Jones (Def Jam Recordings)
- Doechii (Capitol Records/Top Dawg Entertainment)
- GloRilla (Collective Music Group/Interscope Records)
- H.E.R. (RCA Records)
Outstanding Gospel/Christian Album
- “Heart of a Human” — DOE (Life Room Label/RCA Inspiration)
- “Live Breathe Fight” — Tamela Mann (Tillymann Music Group)
- “Still Karen” — Karen Clark Sheard (Karew Records/Motown Gospel)
- “Sunny Days” — Yolanda Adams (Epic Records)
- “The Maverick Way Reimagined” — Maverick City Music (Tribl Records)
Outstanding International Song
- “Close” — Skip Marley (Def Jam Recordings)
- “Hmmm” — Chris Brown feat. Davido (RCA Records/Chris Brown Entertainment)
- “Jump” — Tyla (Epic Records)
- “Love Me JeJe” — Tems (RCA Records/Since ‘93)
- “Piece of My Heart” — Wizkid feat. Brent Faiyaz (RCA Records/Sony Music International/Starboy Entertainment)
Outstanding Music Video/Visual Album
- “Alright” — Victoria Monét (RCA Records/Lovett Music)
- “Alter Ego (ALTERnate Version)” — Doechii, JT (Capitol Records/Top Dawg Entertainment)
- “Boy Bye” — Chlöe (Columbia Records/Parkwood Entertainment LLC)
- “Not Like Us” — Kendrick Lamar (pgLang, under exclusive license to Interscope Records)
- “Yeah Glo!” — GloRilla (Collective Music Group/Interscope Records)
Outstanding Album
- “Alligator Bites Never Heal” — Doechii (Epic Records)
- “Cape Town to Cairo” — PJ Morton (Morton Records/EMPIRE)
- “Coming Home” — USHER (mega/gamma.)
- “Cowboy Carter” — Beyoncé (Columbia Records/Parkwood Entertainment LLC)
- “Glorious” — GloRilla (Collective Music Group/Interscope Records)
Outstanding Soundtrack/Compilation Album
- “Bob Marley: One Love (Soundtrack)” (Tuff Gong/Island Records)
- “Genius: MLK/X (Songs from the Original Series)” (Hollywood Records)
- “Reasonable Doubt (Season 2) (Original Soundtrack)” (Hollywood Records)
- “The Book of Clarence (The Motion Picture Soundtrack)” (Geneva Club under exclusive license to Roc Nation Records, LLC)
- “Wicked: The Soundtrack” (Republic Records)
Outstanding Gospel/Christian Song
- “Church Doors” — Yolanda Adams (Epic Records)
- “Do It Anyway” — Tasha Cobbs (TeeLee Records/Motown Gospel)
- “God Problems (Not By Power)” — (Tribl Records)
- “I Prayed for You (Said a Prayer)” MAJOR. — (NowThatsMAJOR/MNRK Music Group)
- “Working for Me” — Tamela Mann (Tillymann Music Group)
Outstanding Jazz Album
- “Creole Orchestra” — Etienne Charles (Culture Shock Music)
- “Epic Cool” — Kirk Whalum (Artistry Music)
- “Javon & Nikki Go to the Movies” — Javon Jackson and Nikki Giovanni (Solid Jackson Records)
- “On Their Shoulders: An Organ Tribute” — Matthew Whitaker (MOCAT Records)
- “Portrait” — Samara Joy (Verve Records)
Outstanding Soul/R&B Song
- “16 CARRIAGES” — Beyoncé (Columbia Records/Parkwood Entertainment LLC)
- “Here We Go (Uh Oh)” — Coco Jones (Def Jam Recordings)
- “I Found You” — PJ Morton (Morton Records/EMPIRE)
- “Residuals” — Chris Brown (RCA Records/Chris Brown Entertainment)
- “Saturn” — SZA (RCA Records/Top Dawg Entertainment)
Outstanding Hip Hop/Rap Song
- “Mamushi” — Megan Thee Stallion feat. Yuki Chiba (Hot Girl Productions LLC/Warner Music Group)
- “Murdergram Deux” — LL Cool J feat. Eminem (Def Jam Recordings)
- “Noid” — Tyler, the Creator (Columbia Records)
- “Not Like Us” — Kendrick Lamar (pgLang, under exclusive license to Interscope Records)
- “Yeah Glo!” — GloRilla (Collective Music Group/Interscope Records)
Outstanding Duo, Group or Collaboration (Traditional)
- Adam Blackstone & Fantasia — “Summertime” (BASSic Black Entertainment Records/Anderson Music Group/EMPIRE)
- Leela James feat. Kenyon Dixon — “Watcha Done Now” (Shesangz Music, Inc. under exclusive license to BMG Rights Management (US) LLC)
- Maverick City Music feat. Miles Minnick — “God Problems (Not By Power)” (Tribl Records)
- Muni Long & Mariah Carey — “Made for Me” (Supergiant Records/Def Jam Recordings)
- Sounds of Blackness feat. Jamecia Bennett & Buddy McLain — “Thankful” (McLain Music, LLC)
- Flo & GloRilla — “In My Bag” (Island Records)
- GloRilla feat. Kirk Franklin, Maverick City Music, Kierra Sheard, Chandler Moore — “RAIN DOWN
- ON ME” (Collective Music Group/Interscope Records)
- Usher & Burna Boy — “Coming Home” (mega/gamma.)
- Victoria Monét feat. Usher — “SOS” (Sex on Sight) (RCA Records/Lovett Music)
- Wizkid feat. Brent Faiyaz — “Piece of My Heart” (RCA Records/Lovett Music)
Outstanding Original Score for Television/Motion Picture
- “Challengers (Original Score)” (Milan Records)
- “Dune: Part Two (Original Motion Picture Soundtrack)” (WaterTower Music)
- “Star Wars: The Acolyte (Original Soundtrack)” (Walt Disney Records)
- “The American Society of Magical Negroes (Original Motion Picture Soundtrack)” (Back Lot Music)
- “The Book of Clarence (Original Motion Picture Score)” (Milan Records)
Documentary Categories
Outstanding Documentary (Film)
- “Daughters” (Netflix)
- “Frida” (Amazon MGM Studios)
- “King of Kings: Chasing Edward Jones” (Freestyle Digital Media)
- “Luther: Never Too Much” (Sony Music Entertainment/Sony Music Publishing/CNN Films)
- “The Greatest Night in Pop” (Netflix)
Outstanding Documentary (Television)
- “Black Barbie: A Documentary” (Netflix)
- “Black Twitter: A People’s History” (Hulu)
- “Gospel” (PBS)
- “Simone Biles Rising” (Netflix)
- “Sprint” (Netflix)
Outstanding Short Form Documentary (Film)
- “Camille A. Brown: Giant Steps” (American Masters and Firelight Media)
- “Danielle Scott: Ancestral Call” (American Masters and Firelight Media)
- “How to Sue the Klan”
- “Judging Juries”
- “Silent Killer” (Kaila Love Jones Films)
Writing Categories
Outstanding Writing in a Comedy Series
- Ashley Nicole Black — “Shrinking” – “Changing Patterns” (Apple TV+)
- Brittani Nichols — “Abbott Elementary” – “Breakup” (ABC)
- Crystal Jenkins — “No Good Deed” – “Letters of Intent” (Netflix)
- Diarra Kilpatrick — “Diarra From Detroit” – “Chasing Ghosts” (BET+)
- Jordan Temple — “Abbott Elementary” – “Smoking” (ABC)
Outstanding Writing in a Drama Series
- Azia Squire — “Bridgerton” – “Tick Tock” (Netflix)
- Ben Watkins — “Cross” – “Hero Complex” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Francesca Sloane, Donald Glover — “Mr. & Mrs. Smith” – “First Date” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Geetika Lizardi — “Bridgerton” – “Joining of Hands” (Netflix)
- Lauren Gamble — “Bridgerton” – “Old Friends” (Netflix)
- Brandon Espy, Carl Reid — “Mr. Crocket” (Hulu)
- Bree West, Chazitear — “A Wesley South African Christmas” (BET+)
- Juel Taylor, Tony Rettenmaier, Thembi L. Banks — “Young. Wild. Free.” (BET+)
- Rudy Mancuso, Dan Lagana — “Música” (Amazon Prime Video)
- Tina Mabry, Gina Prince-Bythewood, Cee Marcellus — “The Supremes at Earl’s All-You-Can-Eat” (Hulu/Searchlight Pictures)
Outstanding Writing in a Motion Picture
- Barry Jenkins — “The Fire Inside” (Amazon MGM Studios)
- RaMell Ross, Joslyn Barnes — “Nickel Boys” (Orion Pictures/Amazon MGM Studios)
- Steve McQueen — “Blitz” (Apple Original Films)
- Titus Kaphar — “Exhibiting Forgiveness” (Roadside Attractions)
- Virgil Williams, Malcolm Washington — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
Directing Categories
Outstanding Directing in a Comedy Series
- Ayo Edebiri — “The Bear” – “Napkins” (FX/Hulu)
- Bentley Kyle Evans — “Mind Your Business” – “The Reunion” (Bounce TV)
- Robbie Countryman — “The Upshaws” – “Ain’t Broke” (Netflix)
- Tiffany Johnson — “How to Die Alone” – “Trust No One” (Hulu)
- William Smith — “The Vince Staples Show” – “Brown Family” (Netflix)
Outstanding Directing in a Drama Series
- Carl Franklin — “Monsters: The Lyle and Erik Menendez Story” – “Blame It on the Rain” (Netflix)
- Marta Cunningham — “Genius: MLK/X” – “Protect Us” (National Geographic)
- Marta Cunningham — “Genius: MLK/X” – “Who We Are” (National Geographic)
- Paris Barclay — “Monsters: The Lyle and Erik Menendez Story” – “Brother, Can You Spare a Dime?” (Netflix)
- Rapman — “Supacell” – “Supacell” (Netflix)
Outstanding Directing in a Television Movie, Documentary, or Special
- Kelley Kali — “Kemba” (BET+)
- Marcelo Gama — “BET Awards 2024” (BET Media Group)
- Shanta Fripp — “Black Men’s Summit” (BET Media Group)
- Thembi L. Banks — “Young. Wild. Free” (BET+)
- Tina Mabry — “The Supremes at Earl’s All-You-Can Eat” (Hulu/Searchlight Pictures)
Outstanding Directing in a Motion Picture
- Jeymes Samuel — “The Book of Clarence” (Sony Pictures)
- Malcolm Washington — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- RaMell Ross — “Nickel Boys” (Orion Pictures/Amazon MGM Studios)
- Reinaldo Marcus Green — “Bob Marley: One Love” (Paramount Pictures)
- Steve McQueen — “Blitz” (Apple Original Films)
Outstanding Directing in a Documentary (Television or Motion Picture)
- Bao Nguyen — “The Greatest Night in Pop” (Netflix)
- Dawn Porter — “Luther: Never Too Much” (Sony Music Entertainment/Sony Music Publishing/CNN Films)
- Deborah Riley Draper — “James Brown: Say It Loud” (A&E)
- Jason Pollard, Sam Pollard — “Ol’ Dirty Bastard: A Tale of Two Dirtys” (A&E)
- Nneka Onuorah — “Megan Thee Stallion: In Her Words” (Amazon Prime Video)
Literary Categories
Outstanding Literary Work – Fiction
- “A Love Song for Ricki Wilde” — Tia Williams (Grand Central Publishing – Hachette Book Group)
- “Grown Woman” — Sarai Johnson (Harper – HarperCollins Publishers)
- “Neighbors and Other Stories” — Diane Oliver, Tayari Jones (Foreword) (Grove Atlantic)
- “One of Us Knows: A Thriller” — Alyssa Cole (William Morrow – HarperCollins Publishers)
- “What You Leave Behind” — Wanda M. Morris (William Morrow – HarperCollins Publishers)
Outstanding Literary Work – Nonfiction
- “A Passionate Mind in Relentless Pursuit: The Vision of Mary McLeod Bethune” — Noliwe Rooks (Penguin Press – Penguin Books)
- “Love & Whiskey: The Remarkable True Story of Jack Daniel, His Master Distiller Nearest Green, and the Improbable Rise of Uncle Nearest” — Fawn Weaver (Melcher Media Inc.)
- “Picturing Black History: Photographs and Stories that Changed the World” — Daniela Edmeier,
Damarius Johnson, Nicholas B. Breyfogle and Steven Conn (Abrams Books – Harry N. Abrams) - “The 1619 Project: A Visual Experience” — Nikole Hannah-Jones and The New York Times Magazine (Clarkson Potter – Crown Publishing Group)
- “The Jazzmen: How Duke Ellington, Louis Armstrong, and Count Basie Transformed America” — Larry Tye (Mariner Books – HarperCollins Publishers)
Outstanding Literary Work – Debut Author
- “A Kind of Madness” — Uche Okonkwo (Tin House Books)
- “AfroCentric Style: A Celebration of Blackness & Identity in Pop Culture” — Shirley Neal (HarperCollins Amistad)
- “Grown Woman” — Sarai Johnson (Harper – HarperCollins Publishers)
- “Masquerade” — O.O. Sangoyomi (Forge Books – Tor Publishing Group)
- “Swift River” — Essie Chambers (Simon & Schuster)
Outstanding Literary Work – Biography/Autobiography
- “Bits and Pieces: My Mother, My Brother, and Me” — Whoopi Goldberg (Blackstone Publishing)
- “By the Time You Read This: The Space Between Cheslie’s Smile and Mental Illness” ― Her
Story in Her Own Words — Cheslie Kryst and April Simpkins (Forefront Books) - “Do It Anyway: Don’t Give Up Before It Gets Good” — Tasha Cobbs Leonard, Sarah Jakes Roberts (Foreword) (WaterBrook – Penguin Random House)
- “Lovely One: A Memoir” — Ketanji Brown Jackson (Random House)
- “Medgar and Myrlie: Medgar Evers and the Love Story That Awakened America” — JoyAnn Reid (Mariner Books – HarperCollins Publishers)
Outstanding Literary Work – Instructional
- “Black Joy Playbook: 30 Days of Intentionally Reclaiming Your Delight” — Tracey Michae’l Lewis-Giggets (Ink & Willow – Penguin Random House)
- “I Did a New Thing: 30 Days to Living Free (A Feeding the Soul Book)” — Tabitha Brown (William Morrow – HarperCollins Publishers)
- “Loving Your Black Neighbor as Yourself: A Guide to Closing the Space Between Us” — Chanté Griffin (WaterBrook – Penguin Random House)
- “Radical Self-Care: Rituals for Inner Resilience” — Rebecca Moore (Author), Amberlee Green (Illustrator) (The Quarto Group/Leaping Hare Press)
- “Wash Day: Passing on the Legacy, Rituals, and Love of Natural Hair” — Tomesha Faxio (Clarkson Potter – Crown Publishing Group)
Outstanding Literary Work – Poetry
- “Bluff: Poems” — Danez Smith (Graywolf Press)
- “Good Dress” — Brittany Rogers (Tin House Books)
- “Load in Nine Times: Poems” — Frank X Walker (Liveright Publishing – W.W. Norton & Company)
- “Song of My Softening” — Omotara James (Alice James Books)
- “This Is the Honey: An Anthology of Contemporary Black Poets” — Kwame Alexander (Little, Brown and Company)
Outstanding Literary Work – Children
- “All I Need to Be” — Rachel Ricketts (Author), Tiffany Rose (Illustrator) with Luana Horry (Simon & Schuster Books for Young Readers)
- “Cicely Tyson” — Renée Watson (Author), Sherry Shine (Illustrator) (Amistad Books for Young Readers)
- “Crowning Glory: A Celebration of Black Hair” — Carole Boston Weatherford (Author), Ekua Holmes (Illustrator) (Candlewick Press)
- “My Hair Is a Book” — Maisha Oso (Author), London Ladd (Illustrator) (HarperCollins Publishers)
- “You Can Be a Good Friend (No Matter What!): A Lil TJ Book” — Taraji P. Henson (Author), Paul Kellam (Illustrator) (Zonderkidz – HarperCollins)
Outstanding Literary Work – Youth/Teens
- “American Wings: Chicago’s Pioneering Black Aviators and the Race for Equality in the Sky” —
Sherri L. Smith and Elizabeth Wein (G.P. Putnam’s Sons Books for Young Readers) - “Barracoon Adapted for Young Readers The Story of the Last Black Cargo” — Zora Neale Hurston, Ibram X. Kendi (Adapted by), Jazzmen Lee-Johnson (Illustrator) (Amistad Books for Young Readers)
- “Black Star: The Door of No Return” — Kwame Alexander (Little, Brown Books for Young Readers)
- “Brushed Between Cultures: A YA Coming of Age Novel Set in Brooklyn, New York” — Samarra St. Hilaire (Samarra St. Hilaire)
- “Clutch Time: A Shot Clock Novel (Shot Clock, 2)” — Caron Butler and Justin A. Reynolds (HarperCollins Publishers)
Outstanding Graphic Novel
- “Big Jim and the White Boy: An American Classic Reimagined” — David F. Walker and Marcus Kwame Anderson (Ten Speed Graphic – Penguin Random House)
- “Black Defender: The Awakening” — Dr. David Washington, Mr. Zhengis Tasbolatov (Illustrator), Mr. Billy Blanks (Foreword) (Washington Comix)
- “Gamerville” — Johnnie Christmas (HarperAlley – HarperCollins Publishers)
- “Ghost Roast” — Shawneé Gibbs, Shawnelle Gibbs, Emily Cannon (Illustrator) (Versify – HarperCollins Publishers)
- “Punk Rock Karaoke” — Bianca Xunise (Viking Books for Young Readers)
Podcast Categories
Outstanding News and Information Podcast
- “SundayCivics” (LJW Community Strategies)
- “After the Uprising” (iHeartPodcasts, Double Asterisk)
- “Into America: Uncounted Millions” (MSNBC)
- “Native Land Pod” (iHeartPodcasts, Reasoned Choice Media)
- “The Assignment with Audie Cornish” (CNN Audio)
Outstanding Lifestyle/Self–Help Podcast
- “Balanced Black Girl” (Dear Media)
- “Is This Going to Cause An Argument” (Seven14Seven Media)
- “The R Spot with Iyanla” (Shondaland)
- “Therapy for Black Girls” (iHeartPodcasts)
- “We Don’t Always Agree with Ryan & Sterling” (ABF Creative & Indian Meadows Productions)
Outstanding Society and Culture Podcast
- “Baby, This is Keke Palmer” (Wondery)
- “Club Shay Shay” (Shay Shay Media & The Volume)
- “Higher Learning with Van Lathan and Rachel Lindsay” (The Ringer)
- “We Don’t Always Agree with Ryan & Sterling” (ABF Creative & Indian Meadows Productions)
- “What Now? with Trevor Noah” (Spotify Studios in partnership with Day Zero Productions and Fulwell 73)
Outstanding Sports, Arts and Entertainment Podcast
- “Naked Sports with Cari Champion” (The Black Effect Podcast Network)
- “Nightcap” (Shay Shay Media & The Volume)
- “Questlove Supreme” (iHeartPodcasts)
- “R&B Money Podcast” (R&B Money)
- “Two Funny Mamas” (Mocha Podcasts Network)
Outstanding Podcast – Limited Series/Short Form
- “About the Journey” (Marriott Bonvoy, AT WILL MEDIA & mntra)
- “Squeezed with Yvette Nicole Brown” (Lemonda Media)
- “Stranded” (Broadway Video)
- “The Wonder of Stevie” (Audible, Higher Ground and Pineapple Street Studios)
- “When We Win with Maya Rupert” (Lemonada Media)
Costume Design, Make-Up and Hairstyling Categories
Outstanding Costume Design (Television or Film)
- Ernesto Martinez — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- Megan Coates — “Shirley” (Netflix)
- Gersha Phillips — “The Big Cigar” (Apple TV+)
- Francine Jamison-Tanchuck — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
- Paul Tazewell — “Wicked” (Universal Pictures)
Outstanding Make-up (Television or Film)
- Carol Rasheed — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- Debi Young — “Shirley” (Netflix)
- Rebecca Lee — “Shōgun” (Netflix)
- Matiki Anoff — “The Book of Clarence” (Sony Pictures)
- Para Malden — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
Outstanding Hairstyling (Television or Film)
- Terry Hunt — “Bel-Air” (Peacock)
- Lawrence Davis — “Fight Night: The Million Dollar Heist” (Peacock)
- Nakoya Yancey — “Shirley” (Netflix)
- Brian Badie — “The Penguin” (HBO/Max)
- Andrea Mona Bowman — “The Piano Lesson” (Netflix)
Stunt Category
Outstanding Stunt Ensemble (TV or Film)
- “Cross” (Amazon Prime Video)
- “Grotesquerie” (FX/Hulu)
- “Rebel Ridge” (Netflix)
- “Red One” (Amazon MGM Studios)
- “Them: The Scare” (Amazon Prime Video)
Check out more updates here.
Latest


Samsung Galaxy S25 Series Sets The Standard Of AI Phones As A True AI Companion
Samsung Galaxy S25 series sets the standard of AI phones as a true AI companion …Pioneering the multimodal era with...


5 Things To Expect In Afrobeats In 2025
Afrobeats is poised to reach unprecedented heights in 2025 as Nigerian music continues its remarkable global ascent. The genre’s explosive...


Here Are The 7 Most Ancient Countries On Earth
The oldest countries in the world stand as remarkable testaments to human civilisation, each containing landscapes and monuments that narrate...


Why Self-Reflection Is More Important Than Resolutions
Millions of people embark on a yearly ritual: they sit down with a notebook and pen, eager to craft a...


Nollywood Director, Kemi Adetiba Teases King Of Boys 3
Nollywood director Kemi Adetiba has revealed that another instalment of King of Boys will be released on December 25, 2025....


John McEnroe Says He Can Be The Commissioner Tennis Needs Amid Doping Crisis
Recent doping controversies involving top players have not damaged tennis’s reputation, but John McEnroe believes that appointing a single commissioner...


“Everybody Loves Jenifa” Becomes Nollywood’s Highest-Grossing Film Of All Time
Nollywood filmmaker Funke Akindele has achieved a historic milestone with her latest film, “Everybody Loves Jenifa.” The film has officially...


FG To Premiere TV Series, “Hidden Riches” On Mining Sector On January 25
Nigeria’s Federal Government will launch an ambitious television drama series focused on the nation’s mining sector, premiering “Hidden Riches” on...


Qing Madi Delivers A Soulful Performance Of “Favourite Pyscho”
Rising Afro-RnB sensation Qing Madi launches into 2025 with a mesmerising performance on the prestigious COLOURS platform, showcasing her latest...


Taiwo Awoniyi’s First Goal Of The Season Seals Nottingham Forest’s Win Over Wolves
Taiwo Awoniyi made a triumphant return to Premier League action. He scored in stoppage time to help Nottingham Forest crush...
-Ad-